Explaining the Operation of a 2 Stroke Engine
Share
How does a 2 stoke engine work?
A 2 stroke engine is a type of internal combustion engine that is commonly used in small power tools, motorcycles, and other applications where a lightweight and compact design is required. In this article, we will explore the operation of a 2 stroke engine, its components, and how it differs from a 4 stroke engine.
How a 2 Stroke Engine Works
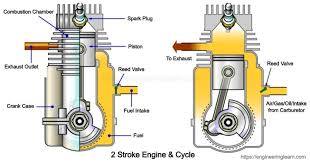
A 2 stroke engine completes a power cycle in just two strokes of the piston, unlike a 4 stroke engine which requires four strokes. These strokes are known as the intake stroke, compression stroke, power stroke, and exhaust stroke.
Components of a 2 Stroke Engine
A 2 stroke engine consists of several key components:
- Piston: The piston moves up and down within the cylinder, compressing the fuel-air mixture and transferring the power to the crankshaft.
- Crankshaft: The crankshaft converts the linear motion of the piston into rotational motion, which is then used to drive the vehicle or power tool.
- Spark Plug: The spark plug ignites the fuel-air mixture, causing combustion and generating power.
- Exhaust Port: The exhaust port allows the burned gases to exit the cylinder after the power stroke.
The Operation of a 2 Stroke Engine
Let's walk through the four strokes of a 2 stroke engine:
- Intake Stroke: As the piston moves downward, it uncovers the intake port, allowing a mixture of fuel and air to enter the cylinder.
- Compression Stroke: The piston moves upward, compressing the fuel-air mixture. At the same time, the spark plug ignites the mixture, causing combustion.
- Power Stroke: The expanding gases from combustion push the piston downward, transferring power to the crankshaft and creating the rotary motion.
- Exhaust Stroke: As the piston moves upward again, it uncovers the exhaust port, allowing the burned gases to escape from the cylinder.
Advantages of 2 Stroke Engines
2 stroke engines offer several advantages over their 4 stroke counterparts:
- Simplicity: 2 stroke engines have a simpler design and fewer moving parts, making them easier to maintain.
- Power-to-Weight Ratio: Due to their lightweight design, 2 stroke engines can produce more power per unit of weight compared to 4 stroke engines.
- Compact Size: The absence of valves and additional components allows 2 stroke engines to have a smaller and more compact size, making them ideal for applications where space is limited.
- Higher RPM: 2 stroke engines can achieve higher revolutions per minute (RPM) compared to 4 stroke engines, resulting in increased power output.
Differences Between 2 Stroke and 4 Stroke Engines
While both 2 stroke and 4 stroke engines are internal combustion engines, they differ in several ways:
- Number of Strokes: As mentioned earlier, 2 stroke engines complete a power cycle in two strokes, whereas 4 stroke engines require four strokes.
- Fuel Mixture: 2 stroke engines require a mixture of oil and fuel to lubricate the moving parts, while 4 stroke engines have a separate oil reservoir and use pure gasoline.
- Fuel Efficiency: 4 stroke engines are generally more fuel-efficient than 2 stroke engines because they burn fuel more effectively and have a dedicated lubrication system.
- Emissions: 2 stroke engines tend to produce more exhaust emissions compared to 4 stroke engines due to the incomplete combustion of the fuel-air mixture.
Common Applications of 2 Stroke Engines
2 stroke engines find wide usage in various applications, including:
- Small Power Tools: Chainsaws, trimmers, leaf blowers, and handheld garden equipment commonly utilize 2 stroke engines due to their compact size and high power-to-weight ratio.
- Motorcycles and Scooters: Many motorcycles and scooters, especially those designed for off-road riding, are equipped with 2 stroke engines for their lightweight and agility.
- Outboard Boat Motors: 2 stroke engines are popular in outboard boat motors due to their simplicity, lightweight, and ability to operate at different angles.
- Generators: Portable generators often employ 2 stroke engines for their small size, portability, and ability to provide reliable power in outdoor settings.
- Snowmobiles: 2 stroke engines are commonly used in snowmobiles due to their high power output and ability to perform in cold weather conditions.
Maintenance and Care
Proper maintenance is crucial to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of a 2 stroke engine:
- Regular Oil and Fuel Mix: It is important to maintain the correct oil-to-fuel ratio specified by the manufacturer to ensure proper lubrication of the engine.
- Spark Plug Maintenance: Regularly inspect and clean the spark plug to ensure a strong spark for efficient combustion.
- Cleaning the Air Filter: A clean air filter allows for proper airflow and prevents contaminants from entering the engine.
- Inspecting and Cleaning the Exhaust Port: Regularly check the exhaust port for carbon buildup and clean it to maintain proper exhaust flow.
- Checking and Adjusting the Carburetor: The carburetor may require periodic adjustments to maintain the correct fuel-air mixture.
Conclusion
A 2 stroke engine's unique design and operating principles make it a popular choice for applications where simplicity, lightweight, and high power-to-weight ratio are essential. Understanding how a 2 stroke engine works, its components, and differences from a 4 stroke engine helps in its maintenance, troubleshooting, and optimizing its performance. While it may have certain drawbacks, the advantages and versatility of 2 stroke engines make them indispensable in various industries and recreational activities.
